The Craig’s test is used to identify femoral anteversion, which is a term used to describe the relative rotation between the femoral shaft and the femoral neck.
How to Perform Craig’s Test
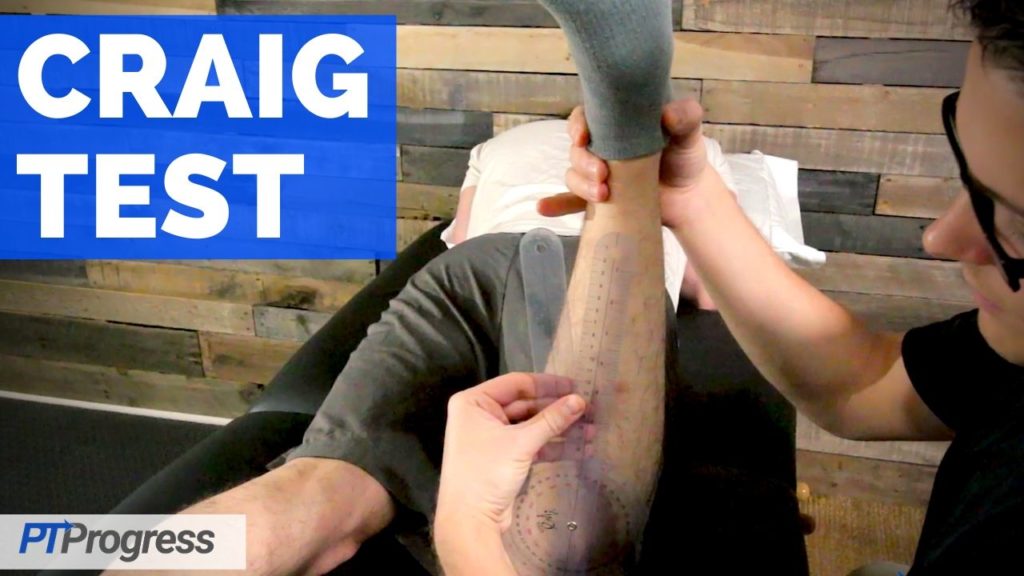
Position of Patient: The patient should be positioned in prone as the examiner stands on the side to be tested. The patient’s knee should also be bent to 90 degrees.
Performance: The examiner should palpate the greater trochanter with one hand and grasp the patient’s lower leg with the other hand. While providing an internal and external rotation of the hip, the examiner should feel the movement of the greater trochanter and stop movement at the position where it is most prominent laterally. Next, measure hip angle with a goniometer to determine the level of hip anteversion.
How to Interpret Craig’s Test
Positive Finding: A positive Craig’s test occurs when hip internal rotation is 15˚ or greater, indicating femoral anteversion. Normal hip anteversion is 8 to 15 degrees.
Test Accuracy / Reliability / Evidence:
Limited evidence

