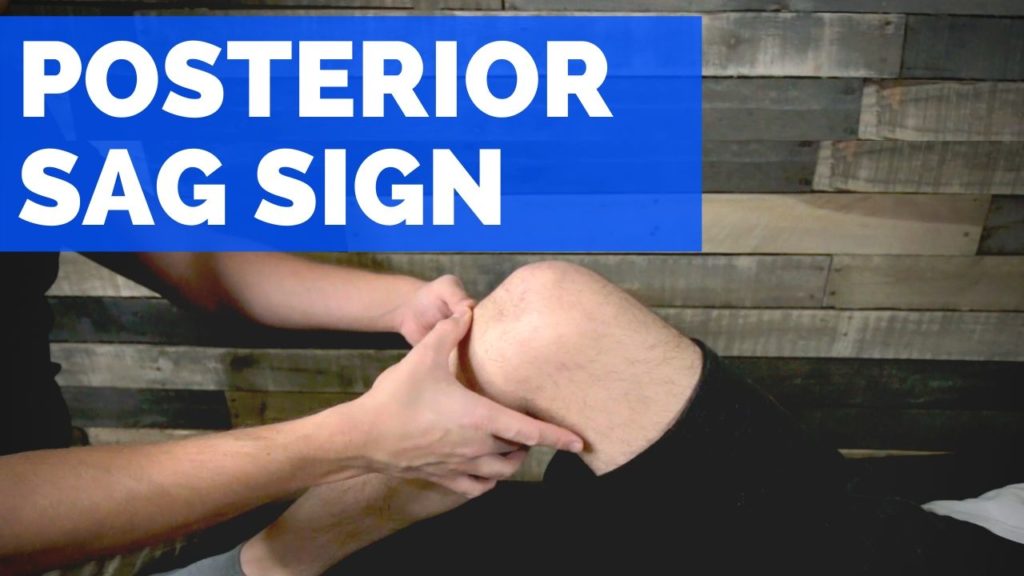
The Posterior Sag Sign is used to assess the integrity of the PCL or posterior cruciate ligament of the knee.
How to Perform Posterior Sag Sign
Position of Patient: The patient is positioned in supine with the hip at 45 degrees and knee at 90 degrees of flexion. The patient’s foot should be flat on the table and may be further stabilized by the examiner’s body.
Performance: The examiner will observe the tibiofemoral joint line for any divot or sagging of the tibia. Further confirmation may be performed by holding the hip and knee at 90 degrees of flexion. While supporting the patient’s heel, observe for any drop or sag of the tibia.
How to Interpret Posterior Sag Sign
Positive Finding: A positive test occurs when the tibia excessively translates posteriorly beyond the neutral alignment with the femur.
Test Accuracy / Reliability / Evidence:
Posterior Sag Sign Sensitivity and Specificity
- Sensitivity = 0.79
- Specificity = 1.0
- +LR = 79
- -LR = .21
Research Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7943523 Rubinstein RA, Jr., Shelbourne KD, McCarroll JR, VanMeter CD, Rettig AC. “The accuracy of the clinical examination in the setting of posterior cruciate ligament injuries.” The American Journal of Sports Medicine. Jul-Aug 1994;
Posterior Sag Sign Video
Interested in more special tests of the knee? Visit our Special Test page for more information.

